VPNs create secure connections over untrusted networks by encapsulating data packets within new headers, forming a tunnel. Protocols like IPsec offer authentication, integrity, and confidentiality via encryption (e.g., AES, 3DES) and key exchange (e.g., IKEv1/v2). IPsec tunnel mode encapsulates the entire original packet, while transport mode encapsulates only the payload. SSL/TLS VPNs encrypt application-layer traffic, often using HTTPS. VPNs can integrate with authentication services (RADIUS, TACACS+) and incorporate advanced features like Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS). NAT traversal and firewall compatibility are crucial for successful deployment.
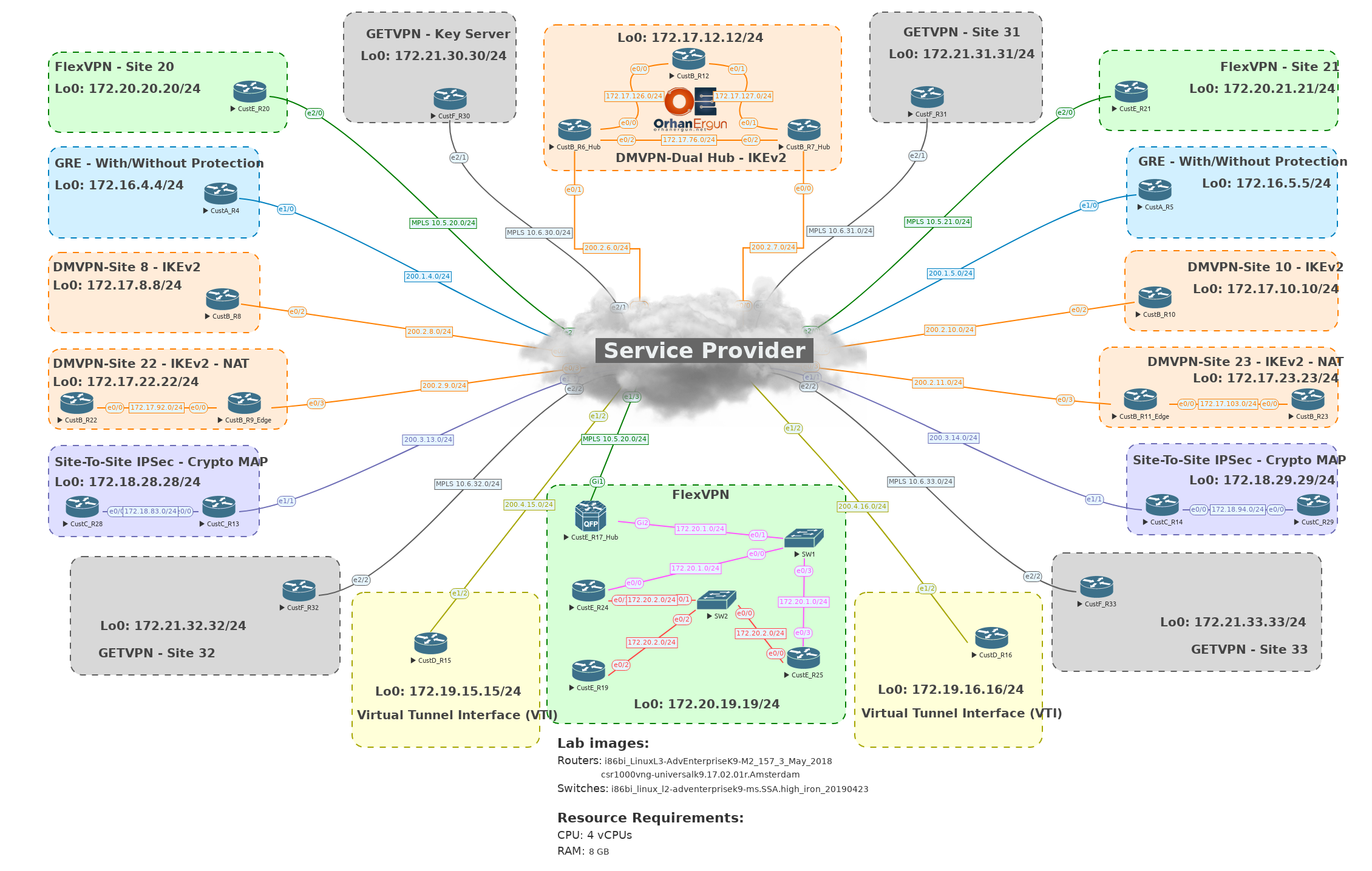
You will be practicing these tasks:
- GRE tunnels
- IPSec/IKEv1
- IPSec/IKEv2
- Site-To-Site VPN using Crypto MAP
- Site-toto-Site IPSec VPN using S-VTI
- DMVPN Phase 1, 2 and 3 with EIGRP
- DMVPN Phase 1, 2 and 3 with OSPF
- GETVPN
- FlexVPN
The default username and password for images used in this course is as follows, however you will hear new passwords during the course if the instructor changes the credentials:
Image name | Username | Password |
IOL images | No username | No password |
CSR1000v | Admin | Admin |
C8000v | Admin | admin |
Viptela devices | Admin | admin |
Windows Server | Administrator | Test123 |
IOS-XR | Admin | Enter new password |
Cisco ASA 802 | no username | no passwd, hit enter |
Cisco ASA 8.4.2, 9.1.5 | no username | no passwd, hit enter |
Cisco ASAv | no username | no passwd, hit enter |
Cisco IPS | cisco | ciscoips123 |
Cisco WSA | admin | ironport |
Cisco ESA | admin | ironport |
Cisco WAAS | admin | default |
Cisco XR9K | Cisco | Cisco |
Cisco NX9K | admin | admin |