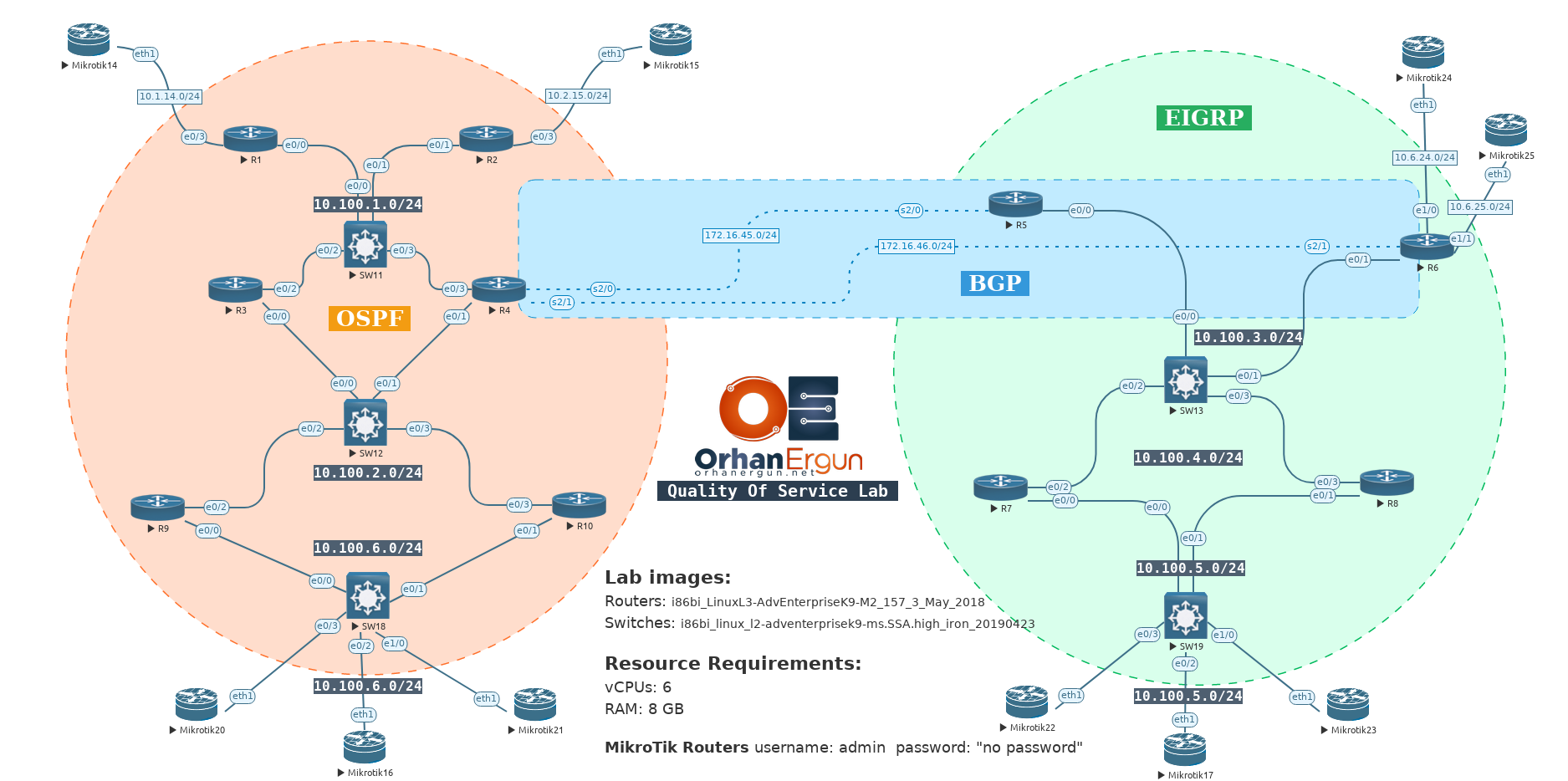
Take control of your network traffic! Our QoS virtual lab lets you master prioritization and optimization techniques for peak application performance. WORKBOOK INCLUDED!
- Category: CCIE Security
Enhance Your IT Skills with OrhanErgun.net Online Training in Networking, Security, and Cloud Technologies.

Take control of your network traffic! Our QoS virtual lab lets you master prioritization and optimization techniques for peak application performance. WORKBOOK INCLUDED!
Our IT rack rental service allows you to access any lab on our website using credits. Here's how it works:
Enjoy flexible and easy access to all our IT labs with our convenient credit system!
Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms prioritize network traffic to ensure optimal performance for critical applications. QoS operates by classifying traffic based on various criteria, such as source/destination IP addresses, port numbers, or application type.
Once classified, traffic is marked using techniques like DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point) or 802.1p, allowing network devices to identify and apply appropriate policies. These policies can include prioritization (giving preference to critical traffic), bandwidth allocation (reserving a specific amount of bandwidth), congestion management (using algorithms like Weighted Fair Queuing or Low Latency Queuing to manage congestion), and traffic shaping (controlling the rate of traffic entering the network).
Effective QoS implementation requires careful planning and configuration, considering factors like network topology, application requirements, and available bandwidth. Furthermore, monitoring and analysis of QoS metrics are essential to ensure that policies are effective, and adjustments can be made as needed.
In this lab you will practice these tasks:
The default username and password for images used in this course is as follows, however you will hear new passwords during the course if the instructor changes the credentials:
Image name | Username | Password |
IOL images | No username | No password |
CSR1000v | Admin | Admin |
C8000v | Admin | admin |
Viptela devices | Admin | admin |
Windows Server | Administrator | Test123 |
IOS-XR | Admin | Enter new password |
Cisco ASA 802 | no username | no passwd, hit enter |
Cisco ASA 8.4.2, 9.1.5 | no username | no passwd, hit enter |
Cisco ASAv | no username | no passwd, hit enter |
Cisco IPS | cisco | ciscoips123 |
Cisco WSA | admin | ironport |
Cisco ESA | admin | ironport |
Cisco WAAS | admin | default |
Cisco XR9K | Cisco | Cisco |
Cisco NX9K | admin | admin |