Learn to build site-to-site VPNs with GRE: Connect your networks with ease and efficiency. WORKBOOK INCLUDED!
- Category: CCIE Security
Enhance Your IT Skills with OrhanErgun.net Online Training in Networking, Security, and Cloud Technologies.

Learn to build site-to-site VPNs with GRE: Connect your networks with ease and efficiency. WORKBOOK INCLUDED!
Our IT rack rental service allows you to access any lab on our website using credits. Here's how it works:
Enjoy flexible and easy access to all our IT labs with our convenient credit system!
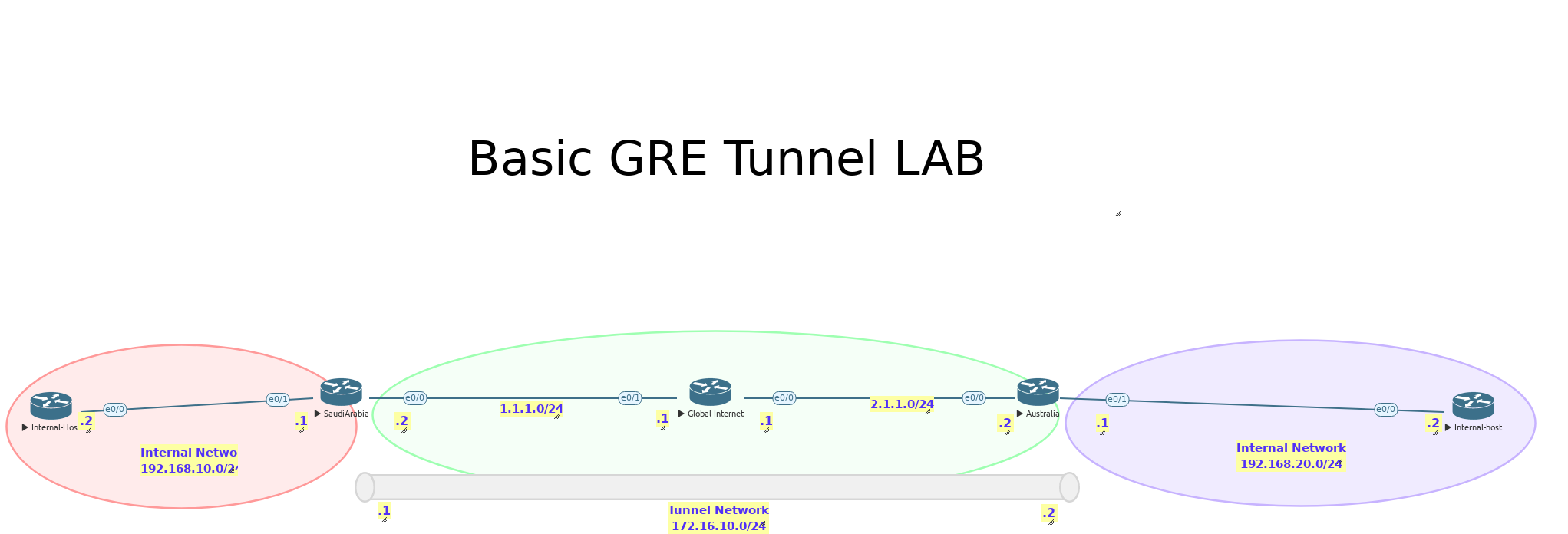
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) tunnels provide a simple and flexible mechanism for encapsulating various network protocols within IP packets, enabling the creation of VPNs.
GRE tunnels establish a virtual point-to-point connection between two endpoints, regardless of the underlying network infrastructure. The original packets, including their headers, are encapsulated within a GRE header and a new IP header, allowing them to be transported over any IP network. This encapsulation allows for the tunneling of non-IP protocols, such as IPv6 or IPX, over an IPv4 network, or vice-versa.
GRE tunnels do not inherently provide encryption, so they are often combined with IPsec to add confidentiality, authentication, and integrity to the tunneled traffic. GRE's simplicity makes it easy to configure and troubleshoot, and its ability to carry diverse protocols makes it a versatile tool for network integration and VPN deployments.
However, the lack of built-in security necessitates careful consideration of security requirements and the potential need for additional security measures. GRE tunnels are commonly used for establishing site-to-site VPNs, connecting remote offices, or creating secure links over untrusted networks.
You might also be interested in these labs:
The default username and password for images used in this course is as follows, however you will hear new passwords during the course if the instructor changes the credentials:
Image name | Username | Password |
IOL images | No username | No password |
CSR1000v | Admin | Admin |
C8000v | Admin | admin |
Viptela devices | Admin | admin |
Windows Server | Administrator | Test123 |
IOS-XR | Admin | Enter new password |
Cisco ASA 802 | no username | no passwd, hit enter |
Cisco ASA 8.4.2, 9.1.5 | no username | no passwd, hit enter |
Cisco ASAv | no username | no passwd, hit enter |
Cisco IPS | cisco | ciscoips123 |
Cisco WSA | admin | ironport |
Cisco ESA | admin | ironport |
Cisco WAAS | admin | default |
Cisco XR9K | Cisco | Cisco |
Cisco NX9K | admin | admin |