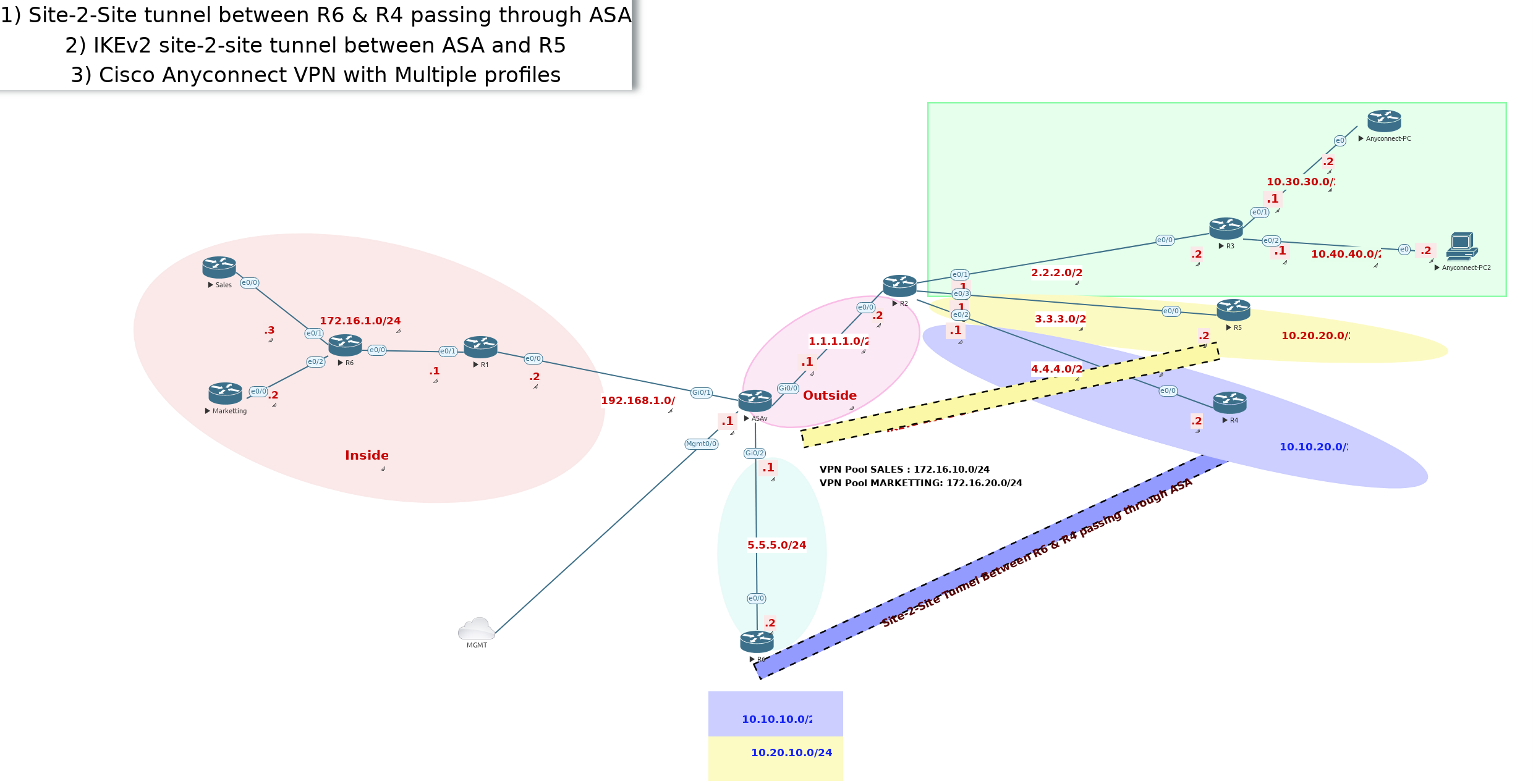
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) enable secure communication between remote networks or users over untrusted networks like the internet. In Cisco ASA (Adaptive Security Appliance) and routers, VPNs are commonly implemented using Site-to-Site VPNs and Remote Access VPNs.
A Site-to-Site VPN establishes a secure, encrypted tunnel between two networks—typically between branch offices and a central data center—using protocols like IKEv1 (Internet Key Exchange version 1) and IKEv2 for secure key exchange and tunnel establishment. ASA firewalls and routers use IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and authentication between the sites. While IKEv1 is widely deployed, IKEv2 offers improved security, faster rekeying, and better resilience to network changes, making it the preferred option in modern networks.
For remote user access, Cisco's AnyConnect VPN allows employees or administrators to securely connect to the network from anywhere. AnyConnect supports multiple VPN profiles, enabling organizations to provide customized access based on user roles, devices, or security policies. It can use SSL VPN (Secure Sockets Layer) or IPsec for encryption, ensuring seamless and secure connectivity.
By combining Site-to-Site VPNs and AnyConnect Remote Access VPNs, organizations can create a flexible and secure network architecture, allowing both branch offices and remote users to securely access critical resources. Configuring these technologies properly on ASA firewalls and routers is essential for enterprise security, compliance, and operational efficiency.
You might also be interested in these labs:
The default username and password for images used in this course is as follows, however you will hear new passwords during the course if the instructor changes the credentials:
Image name | Username | Password |
IOL images | No username | No password |
CSR1000v | Admin | Admin |
C8000v | Admin | admin |
Viptela devices | Admin | admin |
Windows Server | Administrator | Test123 |
IOS-XR | Admin | Enter new password |
Cisco ASA 802 | no username | no passwd, hit enter |
Cisco ASA 8.4.2, 9.1.5 | no username | no passwd, hit enter |
Cisco ASAv | no username | no passwd, hit enter |
Cisco IPS | cisco | ciscoips123 |
Cisco WSA | admin | ironport |
Cisco ESA | admin | ironport |
Cisco WAAS | admin | default |
Cisco XR9K | Cisco | Cisco |
Cisco NX9K | admin | admin |